Dermatitis
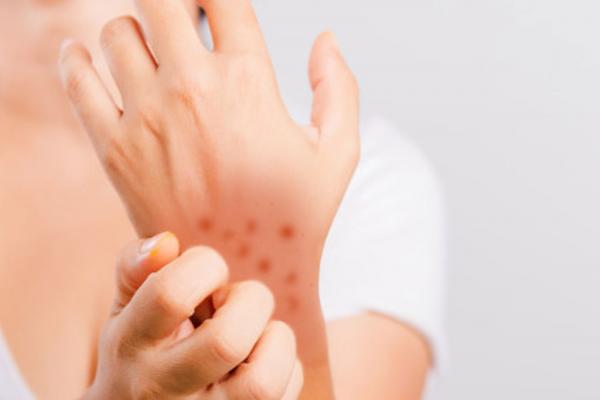
Dermatitis (also known as eczema) is inflammation of the skin, typically characterized by itchiness, redness and a rash. In cases of short duration, there may be small blisters, while in long-term cases the skin may become thickened. The area of skin involved can vary from small to covering the entire body.
Dermatitis includes atopic dermatitis, allergic contact dermatitis, irritant contact dermatitis, seborrhoeic dermatitis and stasis dermatitis. The exact cause of the condition is often unclear. Cases may involve a combination of allergy and poor venous return. The type of dermatitis is generally determined by the person's history and the location of the rash. For example, irritant dermatitis often occurs on the hands of those who frequently get them wet. Allergic contact dermatitis occurs upon exposure to an allergen, causing a hypersensitivity reaction in the skin.
Treatment of atopic dermatitis is typically with moisturizers and steroid creams. The steroid creams should generally be of mid- to high strength and used for less than two weeks at a time, as side effects can occur. Antibiotics may be required if there are signs of skin infection. Contact dermatitis is typically treated by avoiding the allergen or irritant. Antihistamines may help with sleep and decrease nighttime scratching.
Dermatitis was estimated to affect 245 million people globally in 2015, or 3.34% of the world population. Atopic dermatitis is the most common type and generally starts in childhood. In the United States, it affects about 10–30% of people. Contact dermatitis is twice as common in females as males. Allergic contact dermatitis affects about 7% of people at some point in their lives. Irritant contact dermatitis is common, especially among people with certain occupations; exact rates are unclear.
Although the symptoms of atopic dermatitis vary from person to person, the most common symptoms are dry, itchy, red skin. Typical affected skin areas include the folds of the arms, the back of the knees, wrists, face and hands. Perioral dermatitis refers to a red bumpy rash around the mouth.
Dermatitis herpetiformis symptoms include itching, stinging and a burning sensation. Papules and vesicles are commonly present. The small red bumps experienced in this type of dermatitis are usually about 1 cm in size, red in color and may be found symmetrically grouped or distributed on the upper or lower back, buttocks, elbows, knees, neck, shoulders, and scalp. Less frequently, the rash may appear inside the mouth or near the hairline.
The symptoms of seborrhoeic dermatitis, on the other hand, tend to appear gradually, from dry or greasy scaling of the scalp (dandruff) to scaling of facial areas, sometimes with itching, but without hair loss. In newborns, the condition causes a thick and yellowish scalp rash, often accompanied by a diaper rash. In severe cases, symptoms may appear along the hairline, behind the ears, on the eyebrows, on the bridge of the nose, around the nose, on the chest, and on the upper back.
While it has been suggested that eczema may sometimes be an allergic reaction to the excrement from house dust mites, with up to 5% of people showing antibodies to the mites, the overall role this plays awaits further corroboration.
Eczema occurs about three times more frequently in individuals with celiac disease and about two times more frequently in relatives of those with celiac disease, potentially indicating a genetic link between the conditions.
Patch tests are used in the diagnosis of allergic contact dermatitis.
A type of dermatitis may be described by location (e.g., hand eczema), by specific appearance (eczema craquele or discoid) or by possible cause (varicose eczema). Further adding to the confusion, many sources use the term eczema interchangeably for the most common type: atopic dermatitis.
The European Academy of Allergology and Clinical Immunology (EAACI) published a position paper in 2001, which simplifies the nomenclature of allergy-related diseases, including atopic and allergic contact eczemas. Non-allergic eczemas are not affected by this proposal.
Others use the term eczema to specifically mean atopic dermatitis. Atopic dermatitis is also known as atopic eczema. In some languages, dermatitis and eczema mean the same thing, while in other languages dermatitis implies an acute condition and eczema a chronic one.
Source www.wikipedia.org
